1成果简介
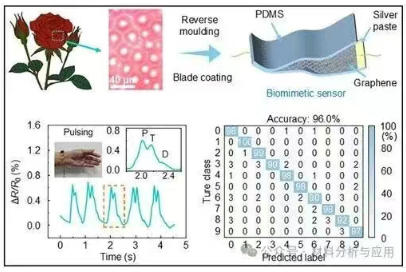
柔性应变传感器在各类高科技领域具有广阔的应用前景,近年来备受关注;然而,在兼顾高性能与简易低成本制造方面仍面临挑战。本文,杭州电子科技大学余森江 副教授团队在《ACS Appl Electron Mater》期刊发表名为“Biomimetic Flexible Strain Sensors with Natural Network Structures for Human Motion Monitoring and Gesture Recognition”的论文,研究受玫瑰花瓣的结构启发,本文通过简易的反向成型与刮刀涂覆技术,开发出高性能石墨烯/聚二甲基硅氧烷(简称Gr/R-PDMS)应变传感器。该天然网络微结构赋予传感器卓越特性:灵敏度高达5256、工作范围广(70%应变)、检测限超低(0.03%)、响应/恢复迅速(205/288毫秒)且耐久性优异(超过15,000次循环)。凭借这些卓越性能,该仿生传感器可精准监测人体多样化动作与生理信号。结合机器学习算法后,该传感器对0-9位数字手势的识别准确率达96.0%,在人机交互与智能可穿戴系统领域展现出巨大潜力。
2图文导读

图1. Preparation and application demonstration of the Gr/R-PDMS sensor. (a) Preparation process of the sensor. (b) Images of the sensor for 70% tensile strain. (c) Images of the sensor for bending and twisting deformations. (d, e) Application demonstration of the sensor for human motion monitoring and gesture recognition.
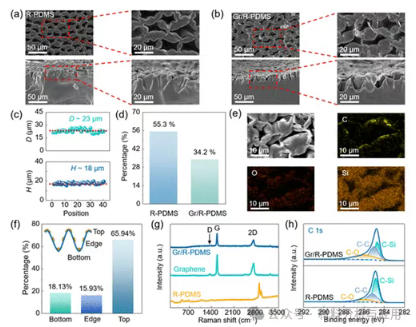
图2. Morphological and structural characterizations of R-PDMS and Gr/R-PDMS samples. (a) SEM images of surfaces and cross sections of R-PDMS. (b) SEM images of surfaces and cross sections of Gr/R-PDMS. (c) Opening size D and depth H of pores at different positions of the R-PDMS. (d) Percentages of opening area of pores for R-PDMS and Gr/R-PDMS. (e) SEM image and EDS element distributions of Gr/R-PDMS. (f) Distribution of graphene in Gr/R-PDMS. (g) Raman spectra of R-PDMS, graphene, and Gr/R-PDMS. (h) XPS spectra of R-PDMS and Gr/R-PDMS for C 1s peaks.
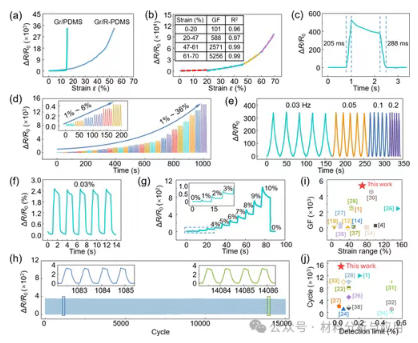
图3. Performances of the Gr/R-PDMS sensor. (a) The relationship between electrical resistance and strain for homogeneous graphene (Gr/PDMS) and rose petal-inspired graphene (Gr/R-PDMS) sensors. (b) Electrical response of the Gr/R-PDMS sensor. The inset shows gauge factor (GF) and linearity (R2) at different strain ranges. (c) Response and recovery time at 7% strain. (d) Change in electrical resistance (five cycles per strain) from 1 to 36% strain. (e) The relationship between electrical resistance and loading frequency at 5% strain. (f) Electrical signal output at extremely low strain of 0.03%. (g) Electrical resistance change by progressive increase in strain from 0 to 10% and finally back to 0%. (h) Electrical response of 15,000 cycles at 5% strain. (i) Comarison of strain range and sensitivity (GF) of the Gr/R-PDMS sensor with the recent literature. (j) Comparison of the detection limit and cycle number of the Gr/R-PDMS sensor with recent literature.
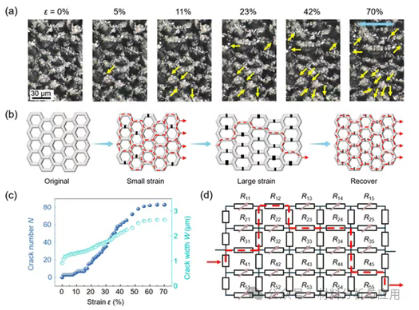
图4. Sensing mechanism of Gr/R-PDMS sensors. (a) In situ evolution of surface topography under uniaxial stretching from 0 to 70%. The yellow arrows represent crack initiations. (b) Schematic diagram of crack evolutions and conductive paths under different strains. (c) Evolutions of crack number N and width W with strain ε. (d) Equivalent circuit diagram of the sensor.
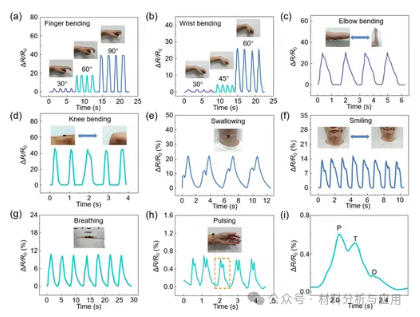
图5. Applications in monitoring human movements and physiological signals. (a, b) Changes in resistance when the finger and wrist are bent for different angles. (c, d) Changes in resistance when the elbow and knee joints are bent for 90°. (e) Changes in electrical resistance during swallowing. (f) Changes in electrical resistance when smiling. (g) Changes in electrical resistance during breathing. (h) Changes in electrical resistance during pulse beating. (i) Enlarged view of a single pulse beating.
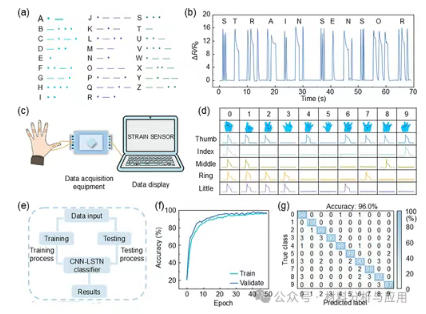
图6. Applications for information expression and gesture recognition of the Gr/R-PDMS sensors. (a) A sequence of 26 international English letters of Morse code. (b) Information expression of “STRAIN SENSOR” through Morse code. (c) Schematic diagram of signal acquisition for gesture recognition. (d) Electrical signals for digital “0” to “9” gestures. (e) Machine learning process for gesture recognition. (f) Evolution of accuracy over 50 epochs. (g) Confusion matrix for gesture recognition of “0” to “9”
3小结
综上所述,受玫瑰花瓣结构启发,通过简易低成本的反向成型与刮刀涂覆策略,成功制备了高性能石墨烯/聚二甲基硅氧烷(Gr/R-PDMS)应变传感器。涂覆的石墨烯主要分布于R-PDMS顶面,形成由玫瑰花瓣拓扑结构调制的六角形网络结构。通过分析不同应变条件下的裂纹演化过程,有效阐释了电子流动的方向性并揭示了传感机制。网络结构的独特设计赋予Gr/R-PDMS传感器卓越性能:高灵敏度、宽工作范围、低检测限、快速响应/恢复及优异的循环稳定性。该传感器已成功应用于人体动作与生理信号检测,并能通过摩斯电码表达信息。借助机器学习技术,Gr/R-PDMS传感器可实现96.0%准确率识别ASL 0-9数字。因此,该传感器在人体动作监测与人机交互领域具有广阔应用前景,为通过仿生结构设计提升传感器性能奠定了基础。
文献:
