1成果简介

硅(Si)作为高能量密度锂离子电池(LIBs)最具前景的负极材料之一,因其在循环过程中体积变化显著而面临商业化挑战。将非晶硅纳米颗粒(SiNP)嵌入多孔碳基体已成为缓解此问题的有效策略,特别是通过近期开发的以硅烷为前驱体的化学气相沉积(CVD)途径。碳骨架的结构特性——如孔径、孔体积和比表面积——至关重要。本文,武汉理工大学屈德宇 教授、刘丹 副教授等在《ACS Appl. Energy Mater 》期刊发表名为“Optimization of Porous Structure on Carbon Host for Silicon/Carbon Anodes in High-Capacity Lithium-Ion Batteries”的论文,研究采用三种模型碳载体:具有单分散微孔的沸石模板碳(ZTC)、均匀分布4.9纳米介孔的CMK-3,以及具有单分散8.3纳米介孔的有序介孔碳(OMC-8)。系统研究了碳载体的多孔结构对硅/碳(Si/C)负极性能的影响。
结果表明,微孔结构能提高硅负载的孔隙利用效率,从而实现高比容量、优异的倍率性能和卓越的循环稳定性。当作为锂离子电池负极时,嵌入ZTC的碳包覆硅(C@Si@ZTC)电极在0.1C充放电条件下展现出2175 mAh g–1的超高比容量,初始库仑效率达87.48%。在0.2C条件下经200次充放电循环后,仍保持1825 mAh g–1的可逆容量。此外,在圆柱形18650电池配置(C@Si@ZTC/石墨||NCM811)中,该电池展现出2143 mAh的容量,并在1C条件下经400次循环后仍保持92.4%的容量保持率。
2图文导读

图1. (a) SEM image of the ZTC. (b) TEM image of ZTC. (c) Nitrogen sorption isotherm and pore size distribution curve of ZTC. (d) SEM image of CMK-3. (e) TEM image of CMK-3. (f) Nitrogen sorption isotherm and pore size distribution curve of CMK-3. (g) SEM image of OMC-8. (h) TEM image of OMC-8. (i) Nitrogen sorption isotherm and pore size distribution curve of OMC-8.

图2. (a) Schematic of silicon deposition into the porous carbon host followed by the carbon coating. HAADF-STEM-EDS elemental mapping images of (b) C@Si@ZTC. (c) C@Si@CMK-3, and (d) C@Si@OMC-8. HRTEM images of the (e) C@Si@ZTC, (f) C@Si@CMK-3, and (g) C@Si@OMC-8. (h, i) Nitrogen sorption isotherm and pore size distribution curve of C@Si@ZTC, C@Si@CMK-3, and C@Si@OMC-8. (j) Percentages of each component in C@Si@ZTC, C@Si@CMK-3, and C@Si@OMC-8.
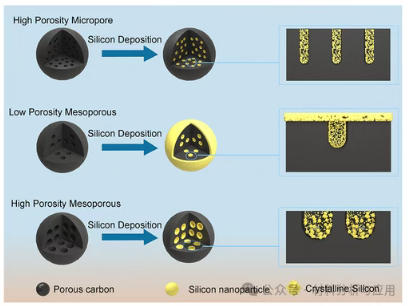
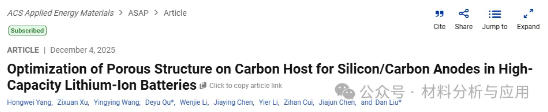
图3. Schematic of silicon deposition behavior in a carbon host with differential porosity.

图4. (a) Cyclic performance at 0.2C (0.1C for the first cycle), (b) Initial discharge–charge voltage profiles at 0.1C, and (c) rate performance of the C@Si@ZTC, C@Si@CMK-3 and C@Si@OMC-8. (d) Nyquist plots of the C@Si@ZTC, C@Si@CMK-3, and C@Si@OMC-8 electrodes after 3 cycles. (e–g) CV curves at various scan rates of C@Si@ZTC, C@Si@CMK-3, and C@Si@OMC-8; (h) the relationship between the peak currents and scan rates in logarithmical format. Galvanostatic intermittent titration technique (GITT) corresponding DLi+C values as a function of (i) lithiation and (j) delithiation states.
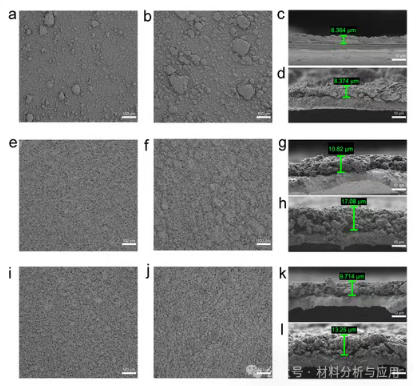
图5. (a, e, i) Top-view SEM images of the C@Si@ZTC, C@Si@CMK-3, and C@Si@OMC-8 electrodes before and (b, f, j) after 200 cycles. (c, g, k) Cross-sectional SEM images of the C@Si@ZTC, C@Si@CMK-3, and C@Si@OMC-8 electrodes before and (d, h, l) after 200 cycles with fully charged (delithiated) state.
图6. (a) Cyclic performances of C@Si@ZTC||NCM811, C@Si@CMK-3||NCM811, and C@Si@OMC-8||NCM811 full cells at 1C. (b) Comparison of the rate performances of the three full cells. (c) Voltage profiles of the C@Si@ZTC||NCM811 full cell in the range of 1C to 4C. (d) Cyclic performance of C@Si@ZTC/Graphite||NCM811, C@Si@CMK-3/Graphite||NCM811, and C@Si@OMC-8/Graphite||NCM811 full cells at 1C.
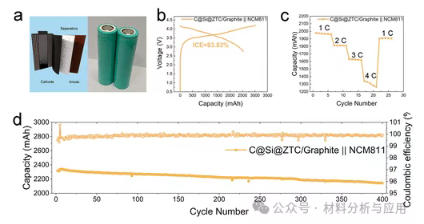
图7. Electrochemical performance of C@Si@ZTC/Graphite|NCM811 cylindrical 18650 batteries. (a) Schematic illustration and digital image of cylindrical 18650 batteries. (b) Initial voltage profiles at 0.1C, (c) rate capability, and (d) cycling performance at 1C.
3小结
综上所述,本研究系统探讨了碳材料纳米结构与通过化学气相沉积法将硅沉积于多孔碳载体中形成的Si/C复合材料性能之间的关联。研究中合成了三种多孔碳模型载体:微孔ZTC、介孔CMK-3和介孔OMC-8,并将其应用于本项研究。微孔ZTC展现出卓越的硅负载孔隙利用效率,使C@Si@ZTC复合材料相比C@Si@CMK-3和C@Si@OMC-8实现更高硅含量(60.1 wt% vs 39.0和34.6 wt%)及更均匀的硅分布。ZTC的结构优势协同作用于最终形成的Si/C负极,显著提升了其比容量、电化学稳定性、电化学转换效率、循环稳定性和倍率性能。在半电池测试中,C@Si@ZTC电极在0.2C倍率下经200次循环后仍保持85.07%容量,可逆容量达1825 mAh g–1。当与NCM811正极配对时,全电池在1C倍率下经200次循环后容量保持率达79.7%。值得注意的是,采用C@Si@ZTC/石墨负极与NCM811正极的圆柱形18650电池,在1C倍率下经400次循环后仍保持2143 mAh放电容量及92.4%容量保持率。本研究为高性能硅碳复合负极设计建立了孔隙结构优化范式。
文献: