1成果简介
柔性钙钛矿太阳能电池(FPSCs)因在蓬勃发展的柔性电子学和便携设备领域具有巨大潜力,引发了广泛的研究热潮。尽管已有大量研究聚焦于FPSCs的性能、柔韧性及稳定性,但三者协同提升仍极具挑战。本文,中国科学院物理所周维亚 研究员在《J. Mater. Chem. A》期刊发表名为“Lightweight and ultra-flexible perovskite solar cells with a “sandwich” perovskite layer based on graphene–carbon nanotube electrodes”的论文,研究成功制备出兼具高性能与卓越稳定性的轻质超柔性钙钛矿太阳能电池(LWUF PSC)。
具体而言,除采用1.5微米厚聚醚酰亚胺薄膜作为柔性基底外, 改进方案主要包含三项创新:设计兼具多功能性的“三明治”结构以充分利用钙钛矿量子点与多晶钙钛矿的优势;采用柔性石墨烯-碳纳米管薄膜电极;以及引入含镍的CuCrO?纳米粒子基空穴传输层以促进光生载流子转移。该器件展现出17.4%的稳定功率转换效率(PCE)及31.1 W g?1的功率密度。特别值得注意的是,在1毫米曲率半径下经受10,000次弯曲循环后,该柔性钙钛矿太阳能电池的光电转换效率仍保持在初始值的92.8%;在相对湿度35%的环境中持续暴露32天后,效率仍维持在初始值的93.0%。该器件独特的结构设计赋予LWUF PSC高光电转换效率、显著的功率密度、优异的机械柔韧性及卓越的环境稳定性,成为迄今为止性能最优异的无铟锡氧化物电极LWUF PSC之一。
2图文导读
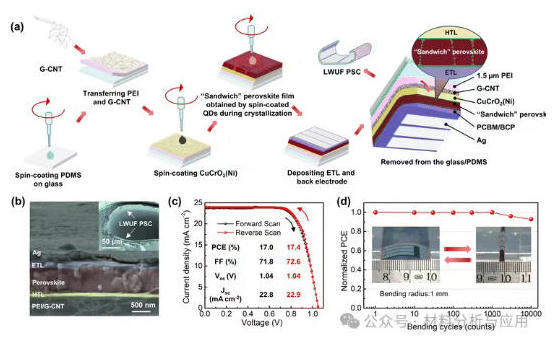
图1、 The process routes and the structural and performance characteristics of the LWUF PSCs. (a) Schematics of the fabrication procedure. (b) Cross-sectional SEM image of the LWUF PSC. The inset shows the SEM image of a LWUF PSC under bending with a curvature radius of 70 μm. (c) J–V curves of the device, recorded in reverse scanning and forward scanning. (d) Mechanical stability of the devices at a bending radius of 1 mm. The inset in (d) shows the digital image of a device under bending cycles.
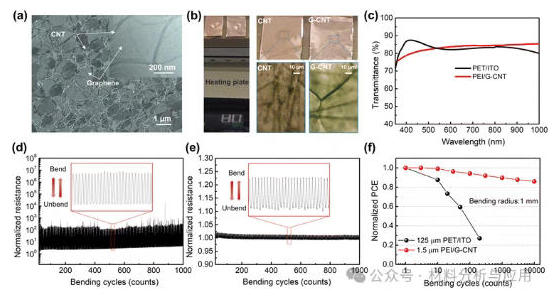
图2、 The microstructure of a G-CNT film and its advantages as a flexible electrode. (a) SEM image of a G-CNT film. The inset shows its HR-TEM image. (b) Moisture resistance investigation of CNT and G-CNT films. (c) Transmittance of PEI/G-CNT and PET/ITO electrode substrates. The dynamic resistances of PET/ITO (d) and PEI/G-CNT (e) electrode substrates in real time during bending cycles with a 1 mm bending radius. (f) Normalized PCE of FPSCs based on PET/ITO and PEI/G-CNT electrode substrates as a function of bending cycles with a bending radius of 1 mm.
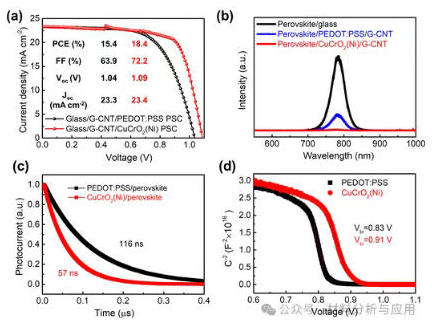
图3、Optimization of the device's efficiency using CuCrO2(Ni) nanoparticles. (a) J–V curves of the PSCs on rigid glass/G-CNT electrode substrates with different HTLs. (b) PL spectra. (c) TPC curves. (d) The Mott–Schottky analysis plot.
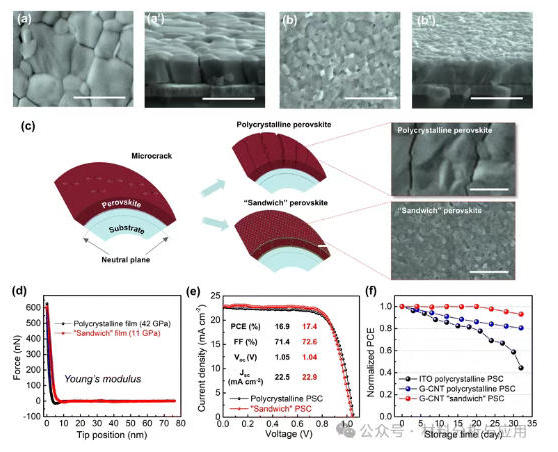
图4 Improvement of the device's performance by the as-designed “sandwich” perovskite architecture. The SEM images of the top and cross-section of the polycrystalline perovskite film (a and a′) and the “sandwich” perovskite film (b and b′). (c) Schematic representation of the relationship between the perovskite structure and the cracks generated during bending. The inset shows SEM images of two kinds of perovskite films after 1000 bending cycles at a curvature radius of 4 mm. (d) Young's modulus of polycrystalline and “sandwich” films. (e) J–V curves of LWUF PSCs. (f) Environmental stability of the PSCs. The scale bar is 1 μm.
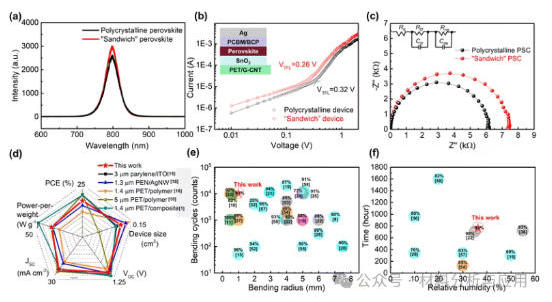
图5 Performance of LWUF PSCs based on polycrystalline and “sandwich” perovskite films. (a) PL spectra of perovskite films. (b) SCLC measurements. (c) Nyquist plots. The insets in (b) and (c) show the electron-only device's architecture and equivalent circuit model, respectively. (d) Comparison of the performance of the LWUF PSC in this work with that of FPSCs reported so far. (e) Mechanical stability of the FPSCs reported so far. (f) Environmental stability of the FPSCs reported so far. Light blue, magenta, gray, and saffron yellow bubbles in (e) and (f) represent ITO electrodes, Ag nanowire electrodes, carbon nanofilm electrodes, and composite electrode-based FPSCs in that order, and the percentages on the bubbles represent the retention rate of PCE after bending or aging.
3小结
本研究通过四方面协同策略,成功制备出兼具高性能与优异稳定性的轻质柔性光伏电池(LWUF PSC)。首先,采用悬浮式超轻质高柔性高透光性导电G-CNT薄膜替代传统氧化物电极,显著提升了光伏电池的柔韧性、机械稳定性及环境适应性。其次,采用1.5μm厚聚乙烯亚胺薄膜作为柔性基板,显著提升柔韧性并大幅减轻器件重量。第三,通过引入CuCrO?(Ni)纳米粒子作为新型高导电性顶层,优化光生载流子传输效率,有效提升光电转换效率。第四,首次设计出由CsPbBr?量子点包裹致密钙钛矿晶粒形成的“夹心式”钙钛矿层作为光吸收层,通过协同效应赋予LWUF PSC卓越的柔韧性、显著的稳定性和高光电转换效率。由此制备的器件实现17.4%的转换效率和31.1 W g?1的功率密度,创下纳米薄膜电极LWUF PSC迄今的最佳性能。
此外,通过量子点钝化形成的夹层结构钙钛矿薄膜,有效解决了超薄基板机械支撑性不足导致的界面接触性能劣化问题。“三明治”钙钛矿的晶粒尺寸从随机分布的200-1000纳米缩小至均匀的100-200纳米。更重要的是,晶界和表面引入的量子点在变形过程中充当晶粒滑动的滚轮,有效抑制了弯曲后的开裂问题。因此,在曲率半径为1毫米的条件下,经10,000次弯曲循环后,LWUF PSC仍保持92.8%的初始功率转换效率。采用不透水“夹心式”钙钛矿吸收层与G-CNT电极后,该柔性钙钛矿太阳能电池在35%相对湿度环境中经32天测试,仍保持93.0%的初始转换效率,展现出卓越的环境稳定性。鉴于该LWUF PSC具备高光电转换效率、高功率密度、卓越的机械柔韧性及显著的环境稳定性,预计可满足更广泛的应用需求,如可穿戴设备、柔性电子器件及航空航天领域。
文献:
