1成果简介
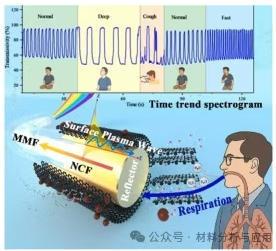
基于多模无芯光纤(MCF)尖端结构中的表面等离子体共振(SPR)原理,本文,上海理工大学卜胜利 教授提出《SENSOR ACTUAT B-CHEM》期刊发表名为“High-performance wearable respiratory sensor based on graphene-oxide-functionalized fiber tip”的论文,研究开发了一种紧凑型高性能光纤传感器,用于湿度与呼吸监测。通过简便的静电层层自组装技术,在探针表面功能化氧化石墨烯(GO)及Fe?O?纳米粒子掺杂氧化石墨烯(MGO),成功形成具有高亲水性与大比表面积的均匀GO/MGO交替多层结构。该传感器展现出2.633 nm/%RH的最大湿度灵敏度、80 ms的快速响应时间,并在14天内保持稳定运行,灵敏度变化小于5%。制备的典型传感器5可精确检测快速、深度及正常呼吸模式,对应频率分别为1.00Hz、0.16Hz和0.49Hz。通过固定波长强度检测实现的呼吸监测技术,显著降低系统复杂度与成本,在呼吸系统疾病筛查、运动监测及睡眠呼吸暂停检测等可穿戴应用领域展现出巨大潜力。
2图文导读
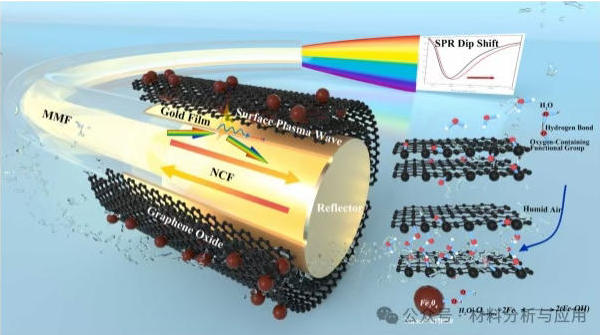
图1. Schematic diagram of the optical fiber SPR humidity sensor functionalized with GO/MGO alternate multilayers.
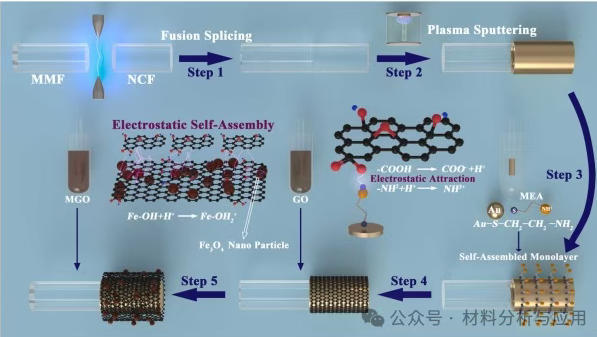
图2. Schematic illustration of the stepwise surface functionalization process for constructing electrostatically self-assembled multilayers of GO/MGO on the sensor surface.
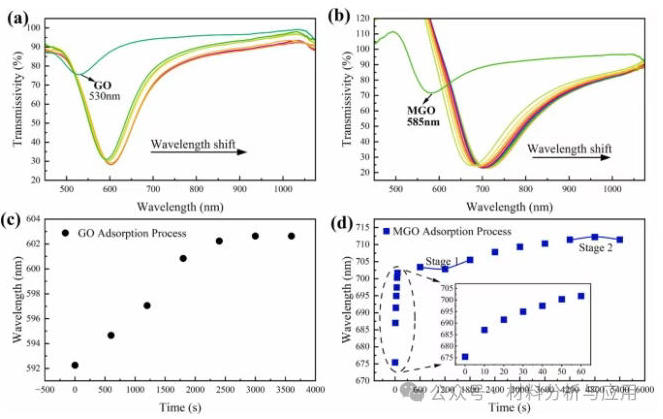
图3. SPR spectral responses during the adsorption processes of GO and MGO: Transmission spectra evolution during (a) GO and (b) MGO adsorption; Wavelength shift over time for (c) GO and (d) MGO.
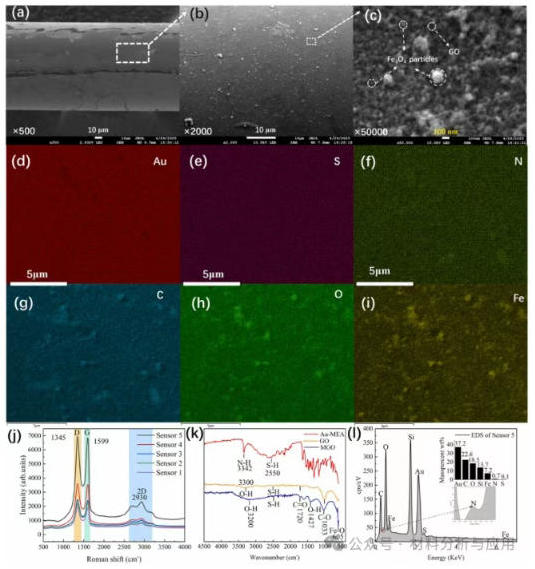
图4. Structural and compositional characterization of the GO/MGO alternate multilayer on the sensor surface: (a–c) SEM images of the as-fabricated typical Sensor 5 at different magnifications (500?×, 2000?×, 50000?×); (d–i) Elemental mapping of Au, S, N, C, O, and Fe; (j) Raman spectra of the as-fabricated five sensors with GO/MGO alternate films; (k) FTIR spectra of Au–MEA, GO, and MGO; (l) EDS elemental composition of Sensor 5.
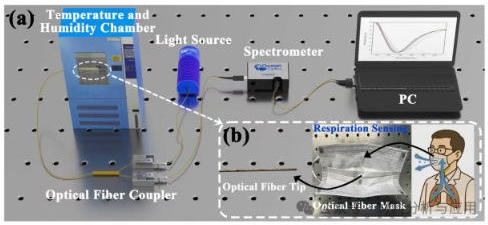
图5. Experimental setup for humidity and respiration sensing: (a) Humidity measurement setup with the sensor installed in the temperature and humidity chamber; (b) Respiration sensing optical fiber tip embedded into a mask.
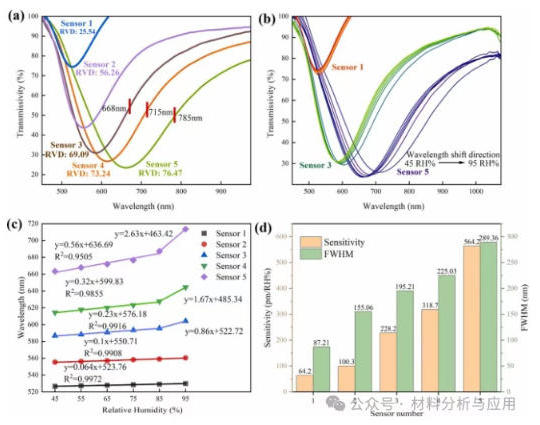
图6. (a) Spectra of Sensors 1–5 corresponding to different numbers of GO/MGO alternate layers (2, 4, 6, 8, 10 bilayers) fabricated via electrostatic self-assembly. (b) Spectra of Sensors 1, 3, and 5 at varying humidity levels. (c) Wavelength shift as a function of relative humidity. (d) Sensitivity and full width at half maximum (FWHM) for Sensors 1–5.
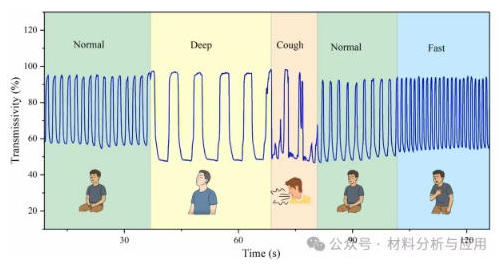
图7、Continuous real-time monitoring at different respiratory modes.
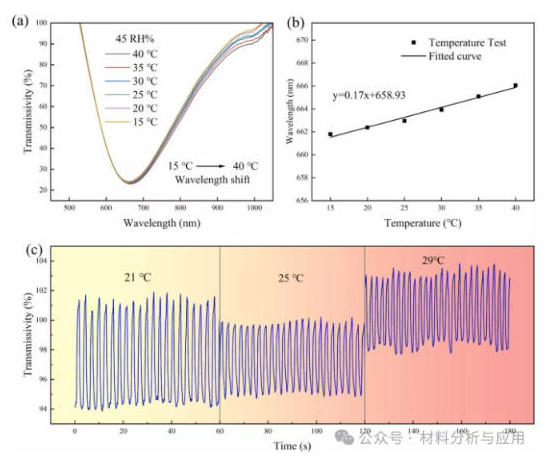
图8. Temperature response of the proposed sensor: (a) Transmission spectra at different temperatures, (b) Resonance wavelength shift as a function of temperature, and (c) Real-time monitoring of respiration at different temperatures.
3小结
在本研究中,我们基于多模无芯光纤结构开发了一种高性能光纤湿度与呼吸传感器,该结构通过静电自组装GO/MGO交替多层膜实现功能化。层层组装技术可精确调控薄膜厚度与成分,相较于传统浸涂法,显著提升了薄膜均匀性与传感性能。该传感器实现最大波长灵敏度2.633 nm/RH%,响应时间仅80毫秒,并在14天长期运行中保持稳定性,灵敏度变化小于5%。该传感器可区分多种呼吸模式,包括快速呼吸、深呼吸、正常呼吸及不规则呼吸(如咳嗽)。与依赖波长偏移检测的湿度传感不同,呼吸传感可通过固定波长下的强度监测实现,从而简化光学装置并降低仪器成本。凭借紧凑结构、高灵敏度、快速响应及卓越稳定性,该传感器在呼吸疾病诊断、运动诱发呼吸分析及睡眠呼吸暂停检测等实时可穿戴应用领域展现出巨大潜力,有望成为新一代智能医疗与个人监测系统的理想候选方案。
文献:
